Explore the hidden world of abandoned farms
The Allure of Abandoned Farms
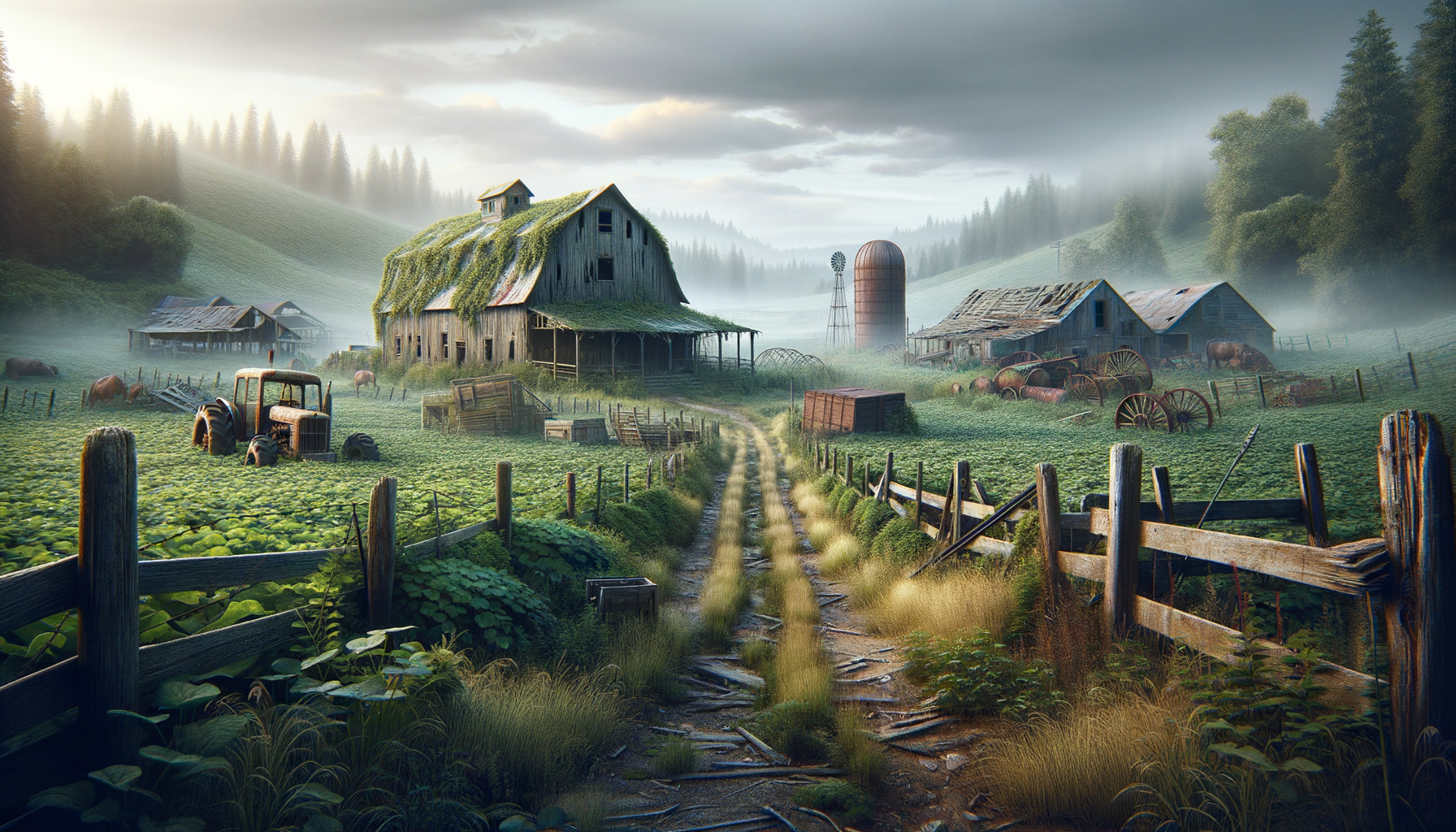
Abandoned farms hold a unique allure that captivates the imagination of many. These neglected landscapes, with their dilapidated barns and overgrown fields, whisper stories of a bygone era. The fascination with abandoned farms often stems from a desire to understand the past and explore the potential for future opportunities. They serve as a reminder of the changing times and the challenges faced by the agricultural industry.
Many abandoned farms are found in rural areas where shifts in economic viability, urbanization, and changes in agricultural practices have led to their desertion. Exploring these sites can reveal insights into historical farming techniques, architectural styles, and the socio-economic conditions of the time. For historians and archaeologists, abandoned farms are treasure troves of information, providing a tangible connection to the past.
Moreover, these farms often become havens for wildlife, as nature reclaims the land. This natural regrowth can offer ecological benefits, contributing to biodiversity and serving as a refuge for various species. For those interested in conservation, abandoned farms present an opportunity to study natural reclamation processes and the role of human intervention in environmental restoration.
Historical Significance and Cultural Heritage
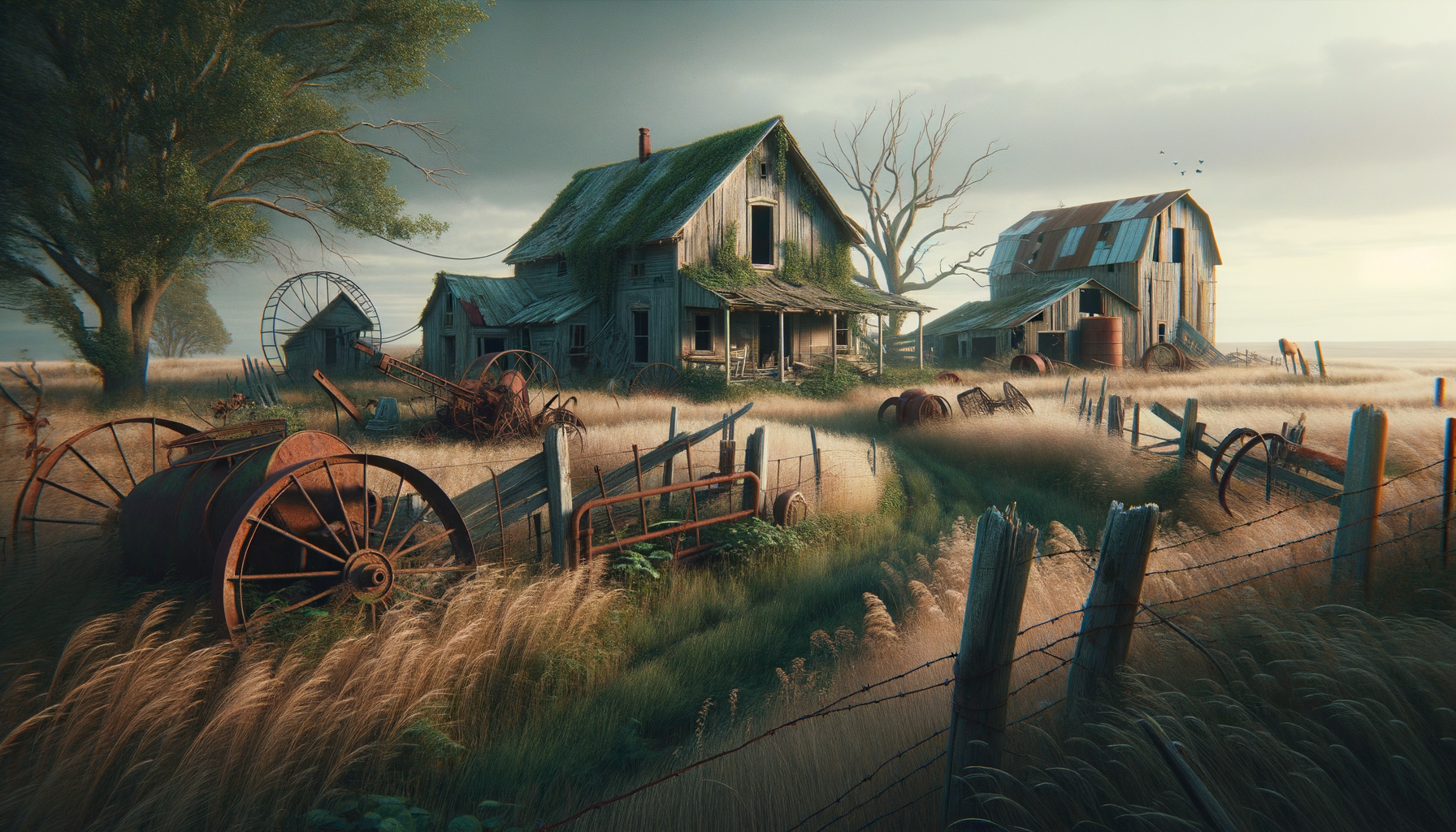
The historical significance of abandoned farms cannot be overstated. These sites often represent the livelihoods of families who lived and worked the land for generations. They are a testament to the agricultural practices and community life of the past. The architecture of farmhouses, barns, and outbuildings reflects the cultural heritage of the region, showcasing traditional building techniques and materials.
Preserving the cultural heritage of abandoned farms is crucial for maintaining a connection to our roots. Restoration projects can revitalize these sites, transforming them into educational centers or community spaces that honor the legacy of those who came before us. By repurposing these farms, we can create a bridge between the past and the present, ensuring that future generations understand the importance of agriculture in shaping our society.
Abandoned farms also serve as a source of inspiration for artists and writers. The picturesque decay and haunting beauty of these sites evoke a sense of nostalgia and mystery, often becoming the subject of paintings, photographs, and literature. This artistic exploration helps to keep the stories of these farms alive, inviting others to appreciate their historical and cultural significance.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities
The abandonment of farms is often driven by economic challenges. Changes in market demand, fluctuating commodity prices, and increased competition can make farming unsustainable for some. Additionally, younger generations may choose to pursue opportunities in urban areas, leaving family farms without successors. These economic pressures contribute to the decline of rural communities and the rise of abandoned farms.
However, abandoned farms also present economic opportunities. With the growing interest in sustainable agriculture and organic farming, these sites can be revitalized to support new agricultural ventures. Entrepreneurs and investors can transform neglected land into thriving enterprises, contributing to local economies and creating jobs. Initiatives such as community-supported agriculture (CSA) and agritourism can breathe new life into these farms, attracting visitors and fostering a sense of community.
Furthermore, government programs and grants can provide financial support for the rehabilitation of abandoned farms. By investing in rural development, policymakers can encourage the preservation and revitalization of these sites, promoting economic growth and sustainability in the agricultural sector.
Environmental Impact and Restoration
Abandoned farms can have a significant environmental impact, both positive and negative. On the one hand, the cessation of farming activities allows ecosystems to recover, promoting biodiversity and providing habitats for wildlife. This natural succession can lead to the restoration of native plant species and the improvement of soil health.
On the other hand, abandoned farms may also pose environmental challenges. The presence of old machinery, chemical residues, and deteriorating structures can lead to pollution and soil degradation. Addressing these issues requires careful planning and management to ensure that the land is restored in an environmentally responsible manner.
Restoration projects can focus on sustainable land management practices, such as reforestation, wetland restoration, and soil conservation. These efforts can enhance the ecological value of abandoned farms, turning them into valuable natural resources. Collaborating with environmental organizations and local communities can facilitate the successful restoration and preservation of these sites.
The Future of Abandoned Farms
The future of abandoned farms is filled with potential. As interest in sustainable living and local food systems continues to grow, these sites offer opportunities for innovation and creativity. By reimagining the use of abandoned farms, we can address contemporary challenges such as food security, climate change, and rural depopulation.
Innovative approaches to farming, such as permaculture and agroforestry, can be implemented on abandoned farms to create resilient and productive landscapes. These practices focus on mimicking natural ecosystems, promoting biodiversity, and enhancing the sustainability of agricultural systems. Abandoned farms can become hubs for research and experimentation, driving advancements in sustainable agriculture.
Community involvement is key to the successful transformation of abandoned farms. By engaging local residents, stakeholders, and organizations, we can develop collaborative solutions that benefit both people and the environment. Through education and outreach, we can inspire a new generation of farmers and land stewards, ensuring that abandoned farms are not just relics of the past, but vital components of a sustainable future.