Explore the hidden world of abandoned farms
The Historical Significance of Abandoned Farms
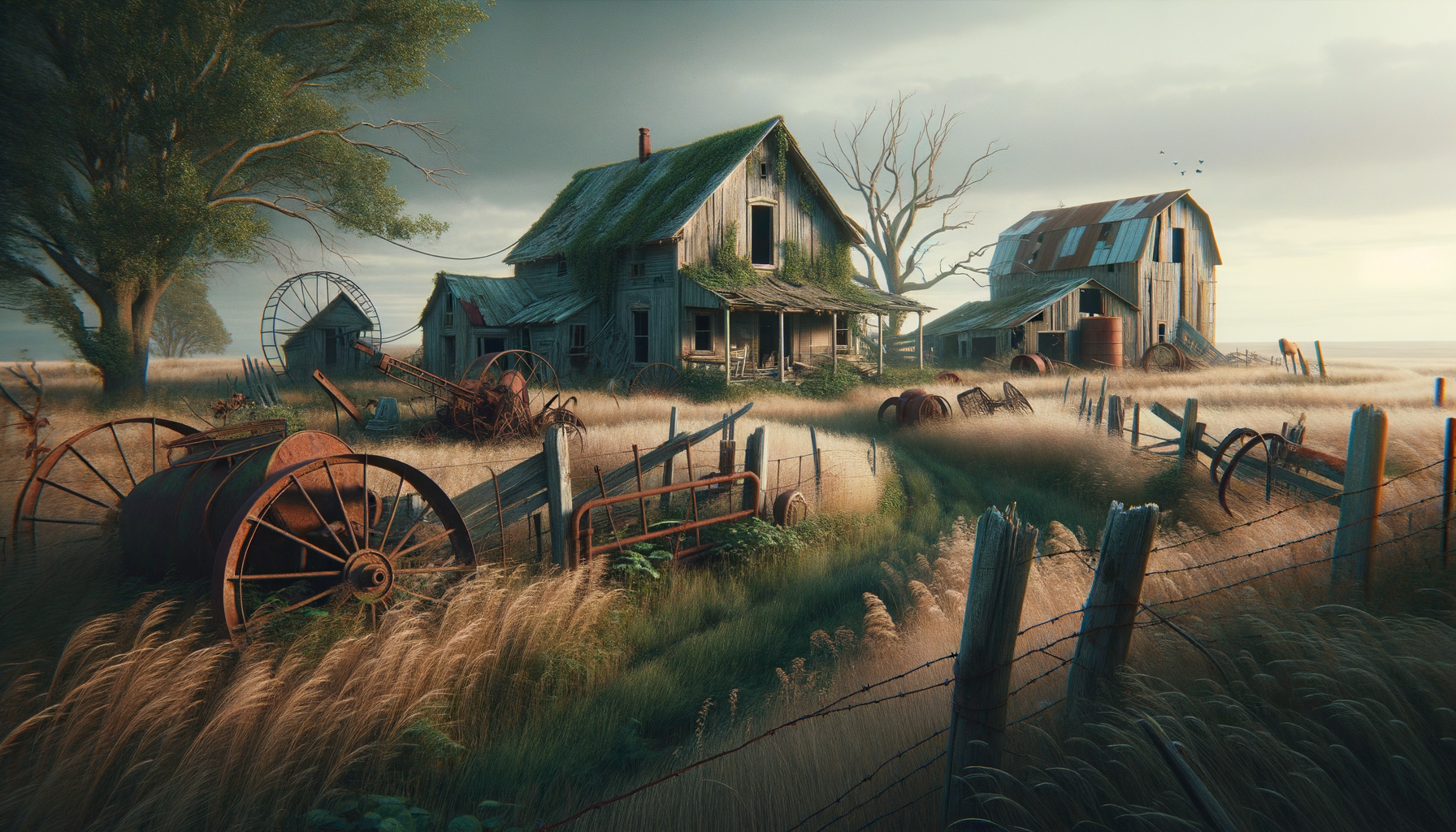
Abandoned farms are more than just remnants of the past; they are historical markers that tell stories of bygone eras. These sites often hold the key to understanding the agricultural practices, economic conditions, and social structures of their time. For instance, during the Great Depression, many farms were abandoned due to economic hardship, leaving behind a legacy of resilience and adaptation. Today, these farms offer a window into the past, allowing historians and enthusiasts to piece together the lives of those who once toiled the land.
Exploring these farms can reveal a tapestry of historical elements, such as old machinery, farmhouses, and barns. Each of these components serves as a testament to the technological advancements and architectural styles of their respective periods. Moreover, abandoned farms can sometimes be linked to significant historical events or movements, such as the Dust Bowl migration or the shift from agricultural to industrial economies.
In essence, abandoned farms are like open-air museums, preserving the narratives of rural communities. By studying these sites, we gain insights into the challenges and triumphs faced by past generations, enriching our understanding of history and its impact on contemporary society.
The Environmental Impact of Abandoned Farms
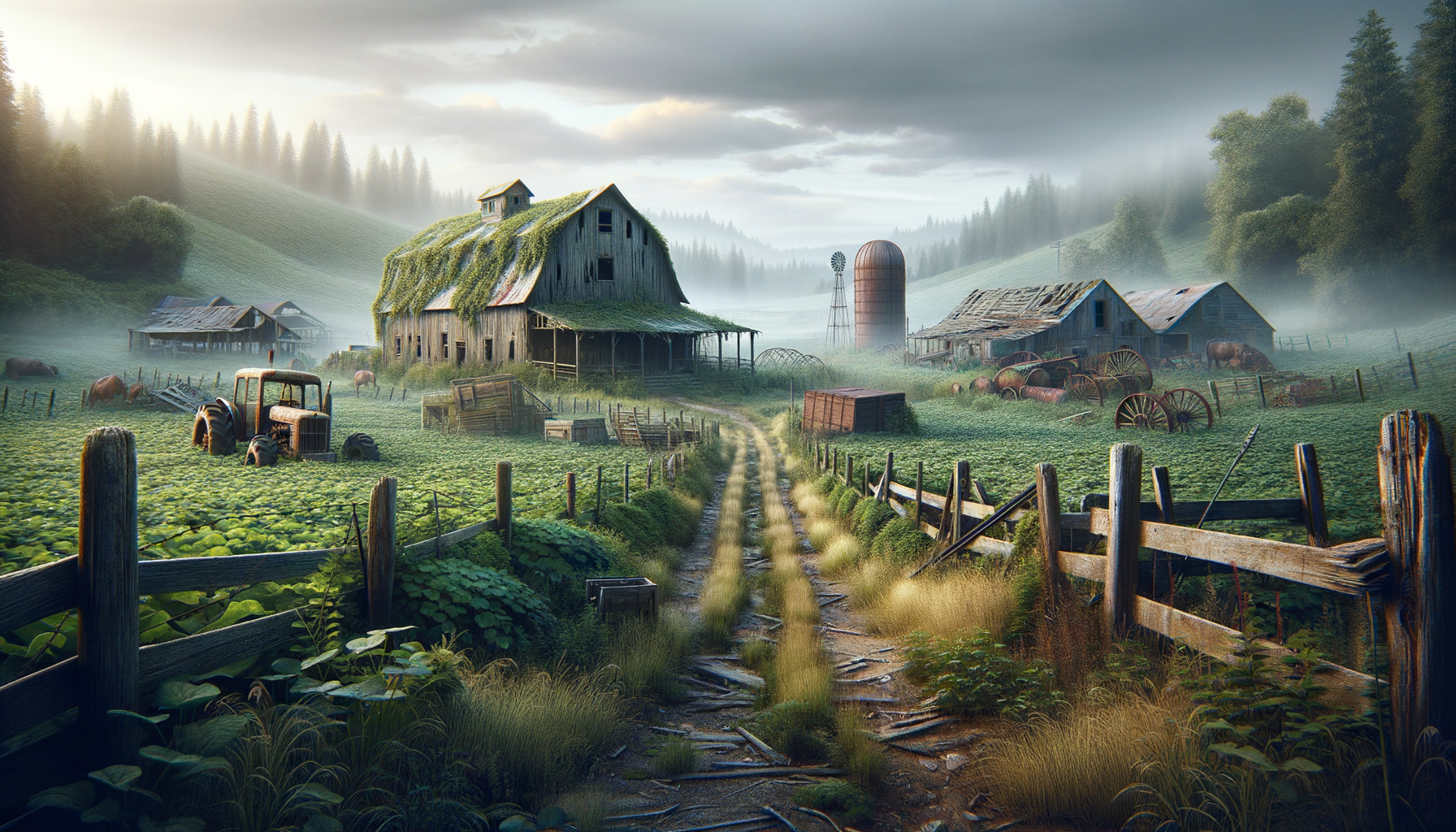
While abandoned farms may seem like mere relics, they play a significant role in the local ecosystem. Over time, nature begins to reclaim these spaces, leading to the development of unique habitats. The absence of human intervention allows for the growth of native plants and the return of wildlife, contributing to biodiversity. In some cases, abandoned farms become crucial sanctuaries for endangered species, offering them a safe haven away from urban development.
However, abandoned farms can also pose environmental challenges. Structures left behind may contain hazardous materials, such as asbestos or lead-based paints, which can leach into the soil and water systems. Additionally, old machinery and equipment can rust and degrade, releasing pollutants into the environment. Addressing these issues requires careful management and remediation to ensure that the natural reclamation process does not inadvertently harm the ecosystem.
Despite these challenges, abandoned farms offer opportunities for environmental restoration and conservation. Initiatives to clean up and repurpose these areas can transform them into community gardens, nature reserves, or educational sites, promoting environmental awareness and sustainability.
Economic Opportunities in Revitalizing Abandoned Farms
Abandoned farms present unique economic opportunities for those willing to invest in their revitalization. With the right approach, these sites can be transformed into profitable ventures, contributing to local economies and creating jobs. One of the most popular trends is converting abandoned farms into agritourism destinations. By offering farm stays, tours, and workshops, these sites can attract visitors interested in experiencing rural life and learning about sustainable farming practices.
Another economic opportunity lies in repurposing abandoned farms for renewable energy projects. The vast open spaces are ideal for installing solar panels or wind turbines, generating clean energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This not only provides a source of income for landowners but also contributes to broader efforts to combat climate change.
Moreover, abandoned farms can be revitalized for agricultural production, focusing on organic and niche markets. With growing consumer demand for locally sourced and organic products, these farms can tap into lucrative markets by offering unique and sustainable produce. This approach not only supports local food systems but also encourages sustainable farming practices.
Social and Cultural Implications of Abandoned Farms
The abandonment of farms often has profound social and cultural implications for rural communities. As families leave their farms, communities can experience a decline in population, leading to the erosion of local traditions and social networks. This can result in a loss of cultural heritage and identity as younger generations move to urban areas in search of better opportunities.
Conversely, abandoned farms can also become centers for cultural revival. Community-driven projects to restore and repurpose these sites can breathe new life into rural areas, fostering a sense of pride and belonging among residents. By hosting cultural events, festivals, and educational programs, these farms can serve as platforms for preserving and celebrating local traditions and crafts.
Furthermore, abandoned farms can play a role in addressing social issues such as food insecurity and unemployment. Community gardens and cooperative farming initiatives can provide fresh produce to local residents, while training programs can equip individuals with valuable skills in agriculture and sustainability.
The Future of Abandoned Farms
The future of abandoned farms holds both challenges and opportunities. As urbanization continues to expand, the fate of these rural spaces remains uncertain. However, with innovative approaches and community involvement, abandoned farms can be transformed into valuable resources that benefit both people and the environment.
One potential future for abandoned farms is their integration into urban planning and development strategies. By preserving green spaces and incorporating them into urban landscapes, cities can enhance their sustainability and resilience. This approach not only provides recreational spaces for residents but also helps mitigate the effects of climate change by promoting biodiversity and reducing urban heat.
Additionally, the rise of digital technology offers new possibilities for abandoned farms. Virtual tours and interactive platforms can bring these sites to a global audience, raising awareness and generating support for their preservation and revitalization. Through collaborative efforts, abandoned farms can become symbols of innovation and sustainability, paving the way for a more harmonious relationship between humans and nature.