Remote Farms: Redefining Agriculture Through Innovation
Introduction to Remote Farms
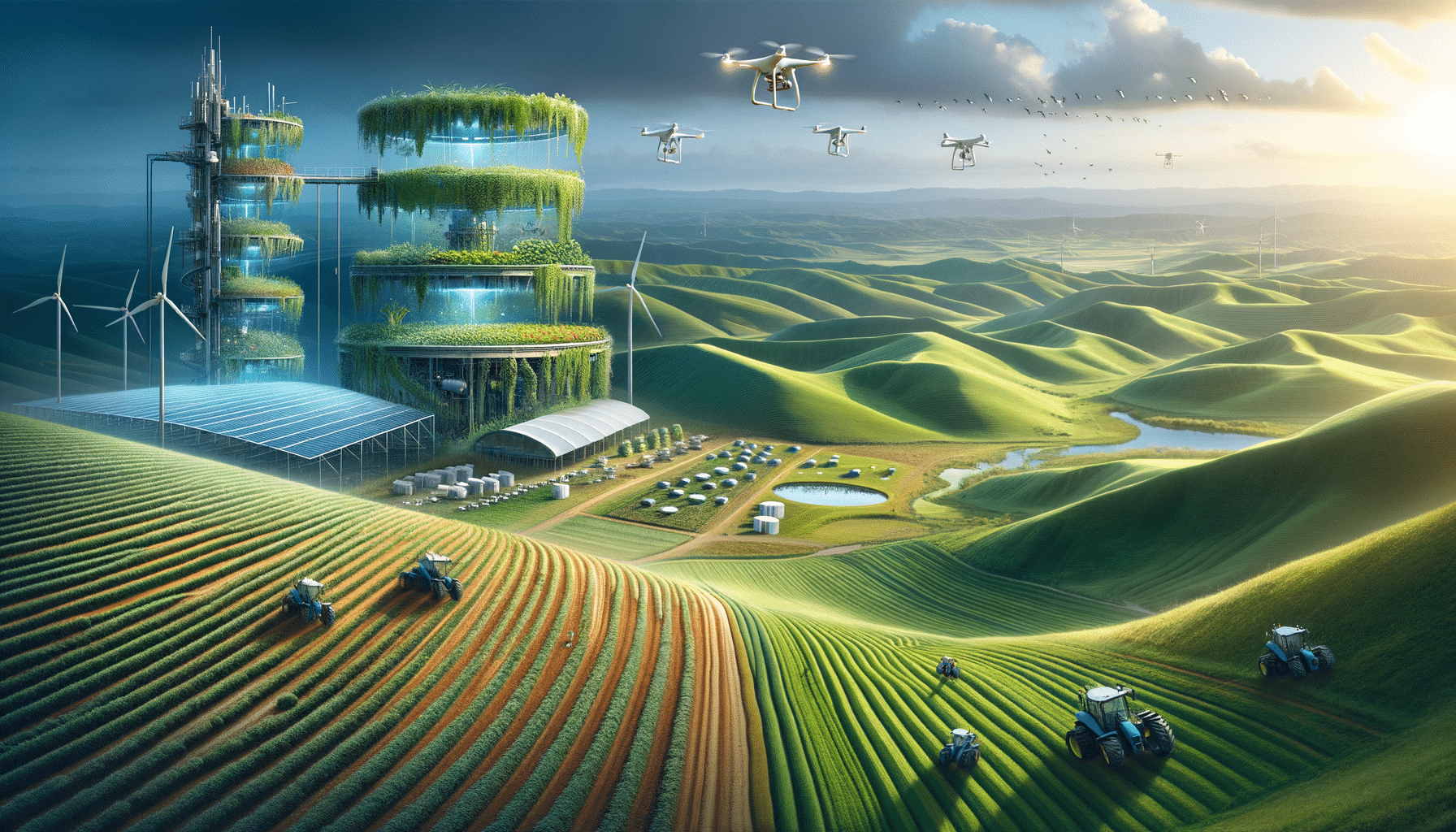
Remote farms are revolutionizing the agricultural landscape by integrating advanced technologies and sustainable practices. These farms are strategically located in challenging environments, where traditional farming might not be feasible. By leveraging innovations such as automated systems and off-grid solutions, remote farms are not only enhancing productivity but also ensuring environmental sustainability. This article delves into the various facets of remote farming, highlighting its significance and potential in reshaping modern agriculture.
The Role of Technology in Remote Farming
Technology plays a pivotal role in the success of remote farms. With the advent of smart farming technologies, these farms can operate efficiently even in isolated locations. Key technological advancements include:
- Automated irrigation systems that optimize water usage.
- Remote sensing devices that monitor soil health and crop conditions.
- Drones for aerial assessment and precision agriculture.
These technologies not only enhance the efficiency of farm operations but also reduce the reliance on manual labor. For instance, automated systems can manage irrigation schedules based on real-time data, ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time. This precision reduces waste and enhances crop yield, making remote farming a viable and sustainable option.
Sustainability in Remote Farms
Remote farms are at the forefront of sustainable agriculture. By adopting eco-friendly practices, these farms minimize their environmental footprint while maximizing productivity. Some sustainable practices include:
- Utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
- Implementing crop rotation and polyculture to maintain soil fertility.
- Reducing chemical usage through integrated pest management.
These practices not only contribute to environmental conservation but also enhance the resilience of remote farms against climate change. By relying on renewable energy, remote farms can operate independently of the grid, reducing carbon emissions and promoting cleaner energy use. Furthermore, sustainable practices ensure that these farms can continue to produce food without depleting natural resources, making them a model for future agricultural endeavors.
Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Farming
While remote farms offer numerous benefits, they also face unique challenges. Isolation can lead to difficulties in accessing resources, labor, and markets. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovation and growth. Solutions such as:
- Developing local supply chains to reduce dependency on distant markets.
- Investing in community-based farming initiatives to pool resources and knowledge.
- Enhancing connectivity through digital platforms for better market access.
By addressing these challenges, remote farms can unlock new opportunities for economic development and food security. The integration of digital platforms can facilitate better communication and collaboration among farmers, enabling them to share knowledge and resources effectively. Moreover, developing local supply chains can bolster regional economies and provide farmers with more control over their produce.
Conclusion: The Future of Remote Farming
Remote farms represent a promising future for agriculture. By combining technological innovation with sustainable practices, these farms offer a blueprint for efficient and resilient food production. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food will increase, making the role of remote farms even more critical. By overcoming challenges and capitalizing on opportunities, remote farms can lead the way in ensuring food security and environmental sustainability for generations to come.


